Introduction
This guide provides instructions on how to set up a brightfield scan profile. Note that slides have to be loaded in order to set up a profile (see "Start up" guide). Please refer to the manuals on the ZMB homepage if you need more detailed information.
-
-
Before starting a large imaging job, it is recommended that you do a full reboot of the system, in the case that you find the microscope on
-
Click the shut-down icon on the desktop, which will turn off the PC
-
Make sure the PC is completely off before continuing
-
Turn off the power putton at the micrscope's side
-
Turn off the whole system with the main power button that is on the desk
-
Wait at least 3 minutes- This critical to have the memory fully rebooted and avoid memory issues for all components inside the microscope
-
Turn the main power back on. This will automatically turn on the PC without the need to touch the PC's on button directly
-
Turn on the power putton at the micrscope's side
-
-
-
The "Scan" tab should be selected
-
Verify that the saving location is on the network drive with the letter X:\ . Otherwise click on "Browse" and select "This PC > SlidescannerStorage (X:)" as a storage location
-
Define the automatic naming of your slides:
-
Select "New".
-
Define your naming template in the "Naming" window
-
Below there are the naming codes, which are letter precided by a % sign. You will put the codes together, as in the example %P_%S_%I, which uses a prefix, a suffix and a counter
-
Check the preview to see the final format and adjust as you need
-
The import of slide names and the automatic assignment of scan profiles to individual slides is possible via a comma-separated file (.csv). See corresponding guide.
-
-
-
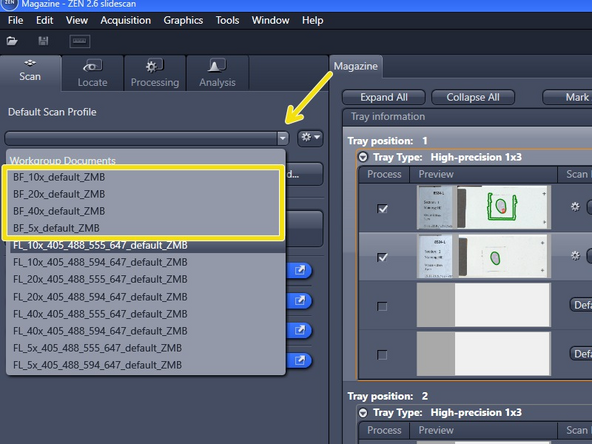
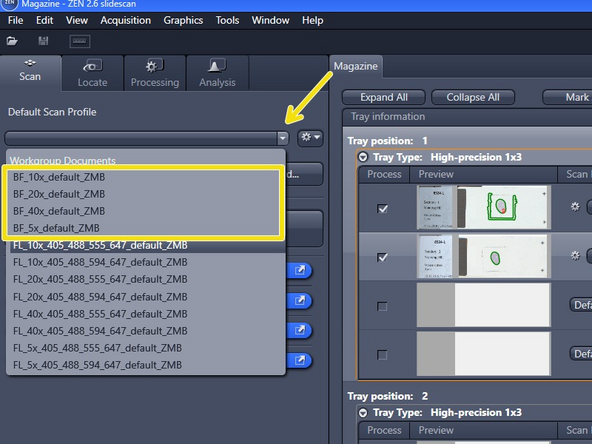
Start with one of the ZMB default profiles (they are already optimized for imaging with a particular objective)
-
Expand the "Default Scan Profile" select a "BF_default_ZMB" scan profile according to the objective you wish to use.
-
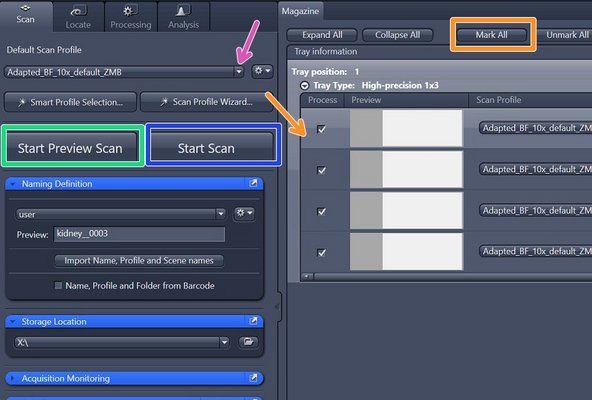
Mark one representative slide of your experiment to adapt the settings of the profile
-
Capture a preview image by clicking on "Start Preview Scan".
-
-
-
Ensure that "Show All (Global)" is checked in the "View" tab.
-
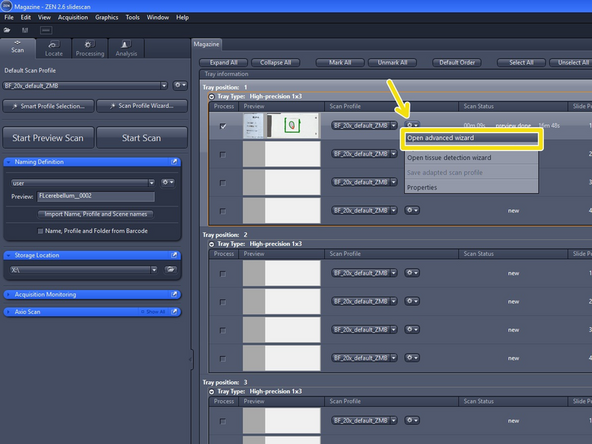
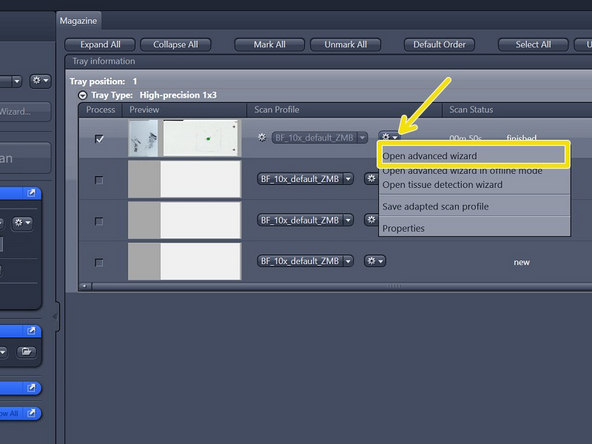
Select "Open advanced wizard" to adjust scan parameters
-
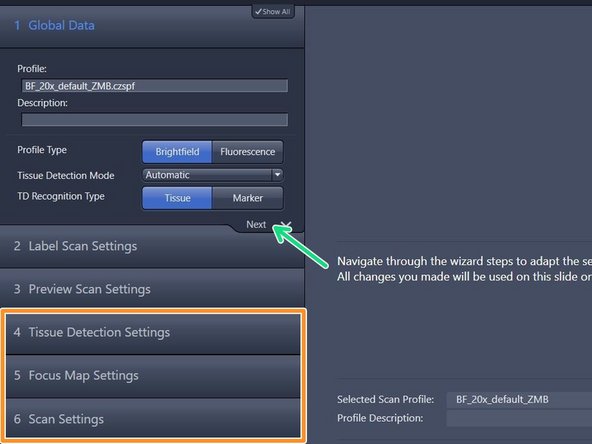
The advanced wizard is composed of 6 steps to adjust scan parameters. Step 1-3 are already optimized for standard slides
-
How to optimize step 4-6 will be explained in the next steps of this guide
-
At the end of each step click on next to proceed
-
-
-
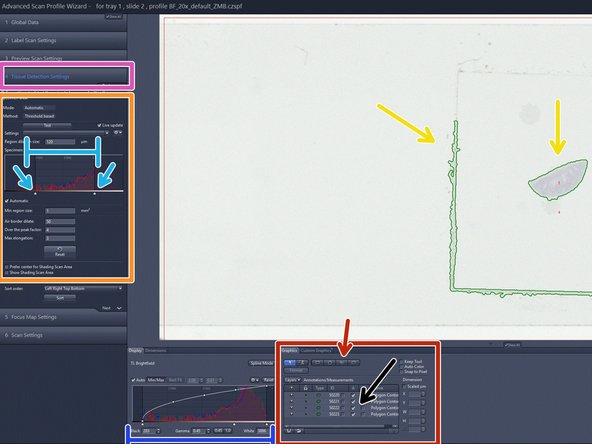
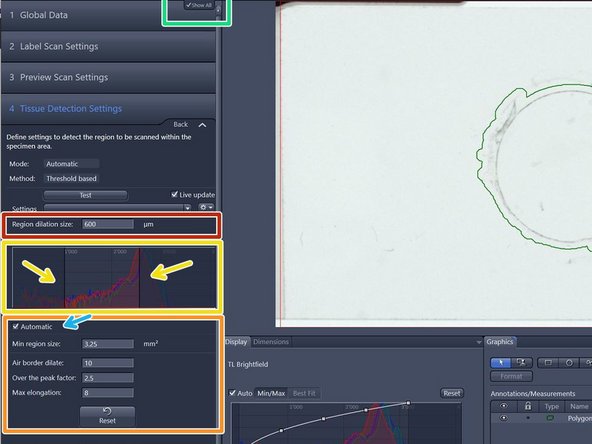
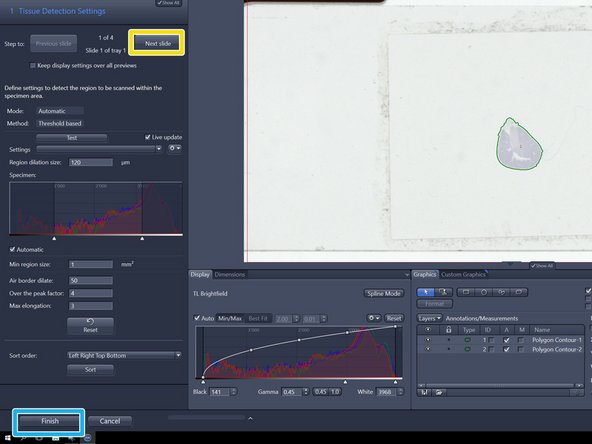
After the preview scan is finished you will be directed to the "Tissue Detection Settings" step.
-
The objects surrounded by a green line are the selected region of interests (ROIs) for scanning
-
They are also listed here
-
Automatic tissue detection is defined on the range shown on the preview histogram and the parameters in the "Tissue Detection Settings" (left) if there is enough contrast in the sample
-
The preview histogram shows the distribution of the intensities of all pixels in the images in RGB. Toggle with the window range of the histogram to adjust the ROIs that are detected
-
It is advisable to play around with the automatic tissues detection, as it will save a lot of time to not have to draw the ROIs manually
-
If you have trouble seeing your sample, you can adjust the contrast on the histogram at the bottom. Note that this just changes how you see the image, and now how the scanner detects the ROIs
-
Manual tissue selection might be necessary for samples with low contrast e.g. fluorescence samples.
-
-
-
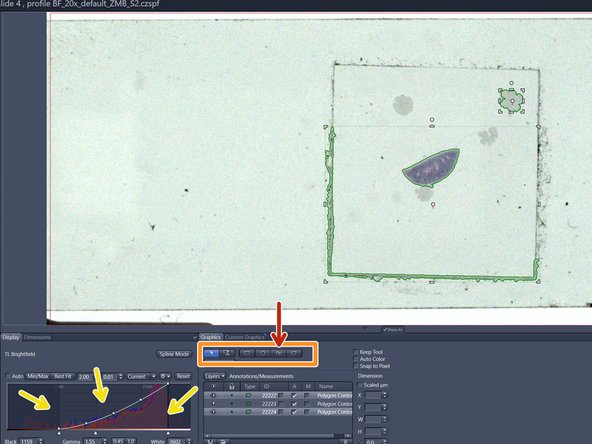
Deactivate "Show All" and activate it again in order to see all options for the automatic tissue detection. (This is a software bug)
-
Modify upper and lower threshold of the "Specimen histogram" to select the ROIs according to intensity values
-
If the "Automatic" checkbox is activated the upper threshold will be determined automatically based on the "Over the peak factor" (a measure for the expected contrast between the glass and tissue)
-
Filter out artifacts with the help of following parameters:
-
" Min region size" : defines the minimum area a ROI should have. Note: The system will not detect regions that are smaller than this value.
-
"Air border dilate": this is a measure to ensure that slide and coverslip edges are not detected as ROIs to be scanned.
-
"Max elongation" can be adjusted to exclude elongated artifacts. Note: Structures that exeed this value for the ratio between the longest side and the shortest side will be excluded.
-
Define a spacing of the border around the detected tissue by adjusting the "Region dilation size" (normally adjusted between 150-200)
-
-
-
If signals are faint it might be necessary to select the ROIs manually with the help of different drawing tools.
-
Adjust the display curve of the histogram for maximal contrast.
-
Draw the wanted regions manually with the tools in the "Graphics" tab.
-
Tip: Draw the outline of the scanning area with the "Draw Spline Contour" tool.
-
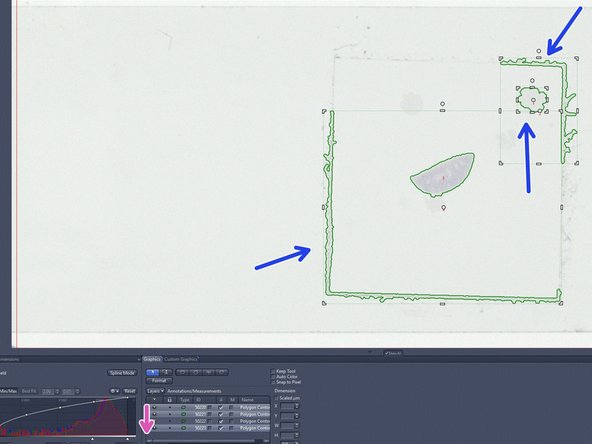
Make sure that there is not too much empty space within your ROI since this could lead to focusing issues.
-
Delete regions that should not be included for scanning: left click to select the regions and right click in order to delete.
-
Optional: Save your ROIs and apply them to similar slides.
-
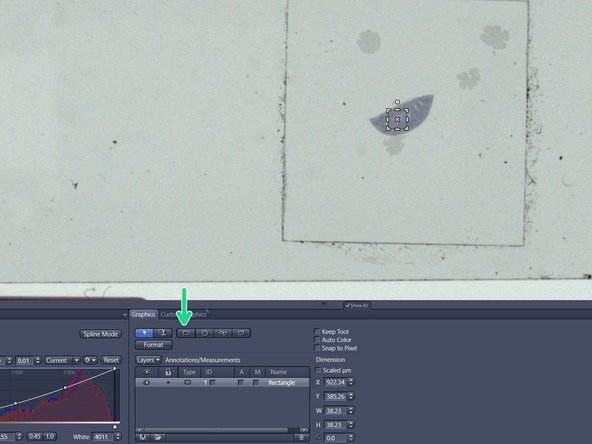
Select a small ROI if you want to test new settings.
-
-
-
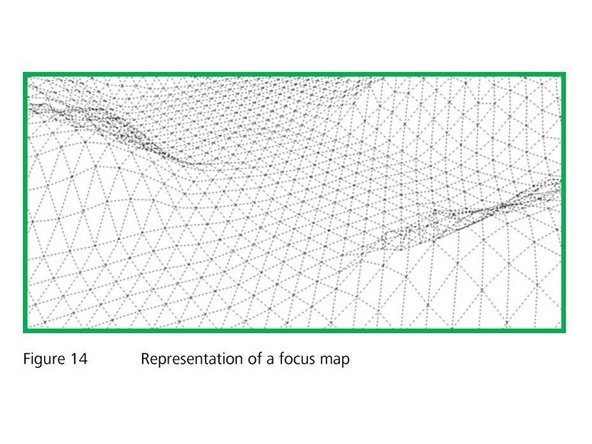
The scanner generates images of your tissues utilizing a "focus map". The focus map is a set of x, y and z coordinates (focus points) that represent the surface of the detected tissue section. While the slide is being scanned, the focus position will change continually following the contour of the focus map.
-
The x & y coordinates of the focus point are defined by a 2D layout of the ROI, and the amount of points will depend on the magnification of the objective. Lower magnifications will have less focus points
-
The z coordinate of the focus points will be done automatically by the scanner. This will be found by the scanner making a series of images at each x-y coordinates, and will compare such images to each other calculating the highest likelihood that each image would be the focus, based on contrast (sharpness)
-
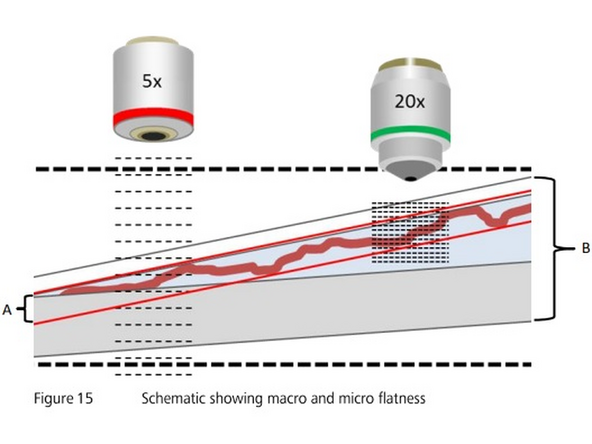
The focus map is created in two steps: In a first step a coarse focus map is created with a low magnifying lens like the 5x objective ("coarse focus"). In a next step the focus map will be refined by a "fine" focus, that is performed with the imaging lens that you have chosen
-
You should pay attention to:
-
The range where the images are made in z, if the range is not correct and does not include the tissue, the scanner wont be able to determine focus, you should also try to keep the focus close to the middle of the range to ensure it works well for other slides.
-
The amount of light being delivered to the sample. The better the illumination, the better the focusing
-
Appropriate focus map settings are important to ensure good focus quality throughout the specimen. Poor set ups can result in bad quality images, or errors and stopping of the acquisition
-
-
-
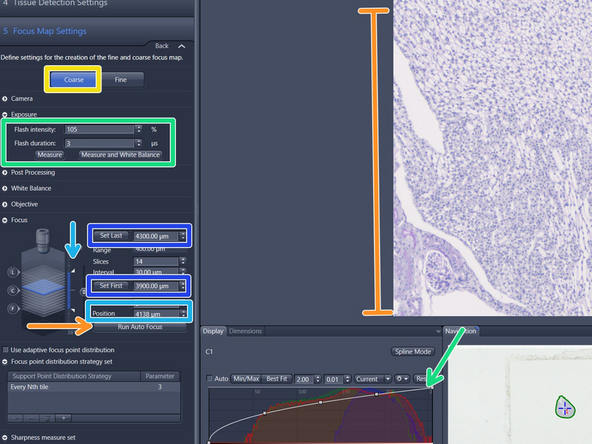
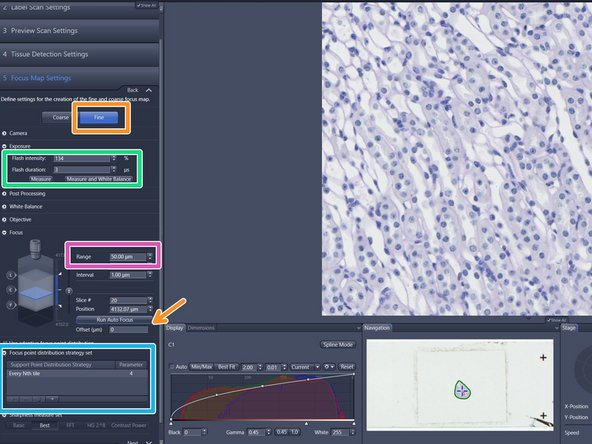
Double click on the "Focus Map Settings" tab make sure "Coarse" mode is active
-
Click "Run Autofocus", and check if the resulting image delivers the expected quality
-
Check the current z-position in the "Position" field. This z-position should be within the range between the values for "Set first" and "Set Last".
-
If the focus is not optimal, focus manually and reset the boundaries by Clicking into the "Position" field and move up/down with the mouse wheel or click on the arrows of the "Focus Position" display and...
-
...ddjust the limits of the capture range so that the focal plane is approximately in the center. Never make the range greater than 500 microns
-
BEAWARE that the capture range can neither be too far (>100 microns) from the standard values, nor wider than ~500 microns. This because the scanner is a widefield system for standard slides, so it knows where the bottom of the slide is and that this system works best with thin sections.
-
The default "Exposure" settings are normally fine. For very bright or dark signals e.g. if the histogram is clipped, it might be necessary to carefully adjust the "Flash intensity"
-
Click again in "Find focus" to check if you changes work as desidre, and if so you repeat checking the autofocusing settings at at different locations of the tissue, and other ROIs inside the slide. If the focus plan is too close to the edge of the rangem then bring it closer to the center by adjusting the limits of the capture range
-
-
-
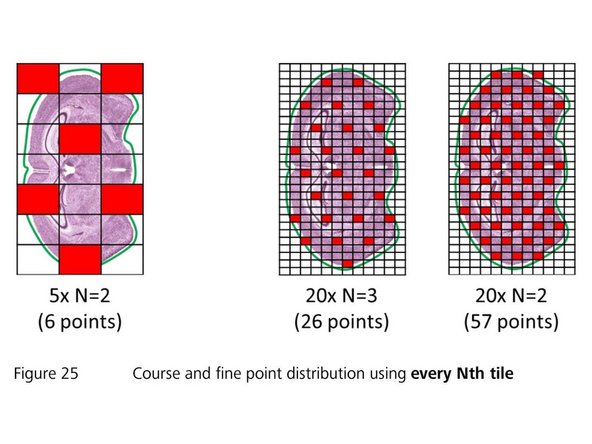
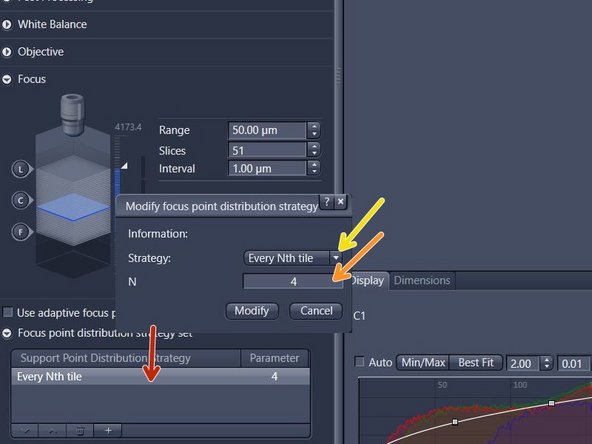
The "Focus Point Distribution Strategy" defines how and how often the autofocus will be executed
-
The default settings work normally fine for standard tissue samples with a medium size
-
For very small, very large or uneven samples, the default settings may have to be adjusted for increased precision or speed:
-
Double-click on the "Focus point distribution strategy" field. Parameters can then be changed in the pup-up window. Click on "Modify" to save the changes
-
For uneven samples, it might be necessary to increase the number of focus points "N". Note: a larger "N" increases the accuracy of the focus map at the cost of a longer scanning time
-
For very large or small tissue sections, selecting another focus strategy might be useful. Change the "Strategy" set via the dropdown menu. Select "Center of Gravity" for very small sections or "Onion Skin" for large specimens
-
The number of focus points should not exceed 400. Restrict the number of focus points by selecting the "Onion Skin"strategy with a maximum of 400 focus points
-
For more information consult the AxioScan Z.1. Application Guide or ask the ZMB staff
-
-
-
Select "Fine" and press "Run Auto Focus"
-
If the focus could not be found increase the focus "Range" and try again
-
The maximum fine focus range should not exeed 100 um. If you need to increase the range further, then the coarse focus settings are not well adjusted
-
The default "Exposure" settings are normally fine. For very bright or dark signals e.g. if the histogram is clipped, it might be necessary to change the "Flash intensity"
-
Define the "Focus map distribution strategy" as described in the previous step
-
The default settings work normally fine for standard tissue specimens with a medium size
-
-
-
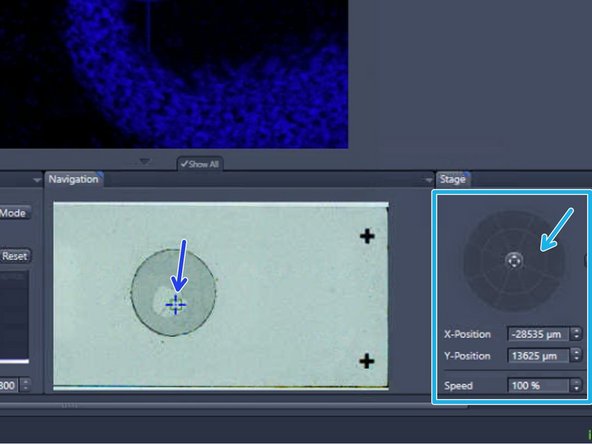
Navigate to diffent positions of your sample:
-
Click inside the slide shown in the "Navigation" tab to move the specimen
-
You can also use the virtual joystick in the "Stage" tab to navigate more precisely
-
Test the "Coarse" and "Fine" focus settings as described previously
-
-
-
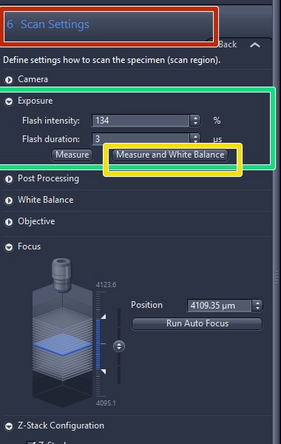
Double click on "Scan Settings"
-
For standard slides (thin tissue sections with a medium brightness) it is usually not necessary to change the default scan settings
-
For optimal illumination you can adjust the white balance values. To do this, navigate to an empty space on your slide and go slightly out of focus so that no debri is taken into account. The press the "Measure While Balance " button. Then navigate back to your tissue/sample
-
The value for "Flash intensity" can be changed for very bright or dark signals e.g. if the histogram is clipped
-
-
-
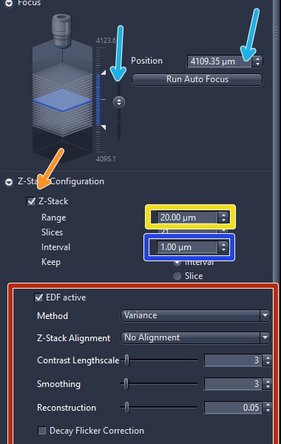
Define a z-stack if the tissue is not flat or very thick. By default the z-stack function is disabled
-
Check "Z-Stack"
-
Set the "Range"
-
Define the z-range by adjusting the upper and the lower limits of the tissue section. To focus manually click on the arrows of the "Focus Position" display or click into the number field and move up/down with the mouse wheel
-
Define an appropriate z-interval
-
Set the z-interval depending on the imaging objective and desired z-resolution e.g. 5 um for the 5x lens, 2 um for 10x lens, 1 um for 20x lens and 0.5 um for 40x lens
-
Check "EDF active" (Extended depth of focus) if you would like to get a 2D projection of your z-stack. As "Method" select either "Variance" or "Maximum intensity projection" . We strongly recommend to use the predefined standard parameters for each method
-
The software will combine the regions of strongest contrast within a given z-stack into one image
-
-
-
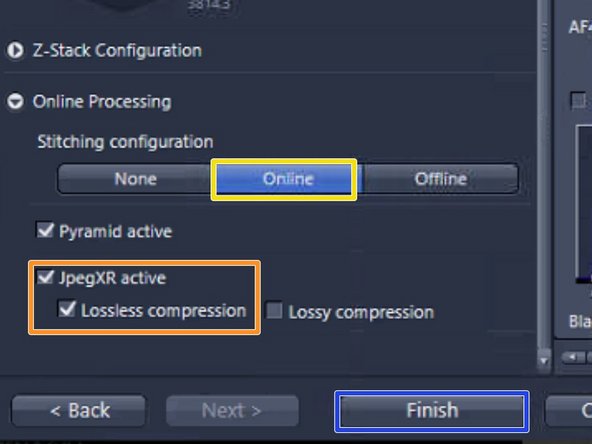
The "Online Processing" expander is the final step of the wizard. For online stitching and imaging with the default format nothing has to be changed
-
"Online" stitching is the default setting and means that the acquired tiles are already stitched during the scan process
-
The files will be saved in the Zeiss file format (.czi). A lossless compression is selected per default. In order to reduce the file size "lossy compression" with a quality of 85% could be selected at the expense of a lower image quality
-
Press "Finish"
-
-
-
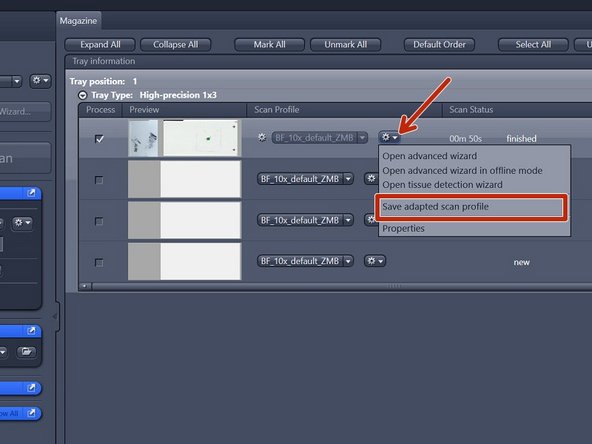
Here is best to first save your settings "Save adapted scan profile", even when you want to make changes, as it is easy to click the incorrect setting and loose your work. Save your profile under:
-
"C:\Users\%username%\Documents\Carl Zeiss\ZEN\Documents\Scan Profiles"
-
The saved profile will be available in your personal "Default Scan Profiles" list and can be applied to other slides
-
-
-
Once all parameters are adjusted test the adapted scan profile on a small ROI of a representative sample. Note: a small ROI has to be manually defined in the "Tissue Detection Settings" step
-
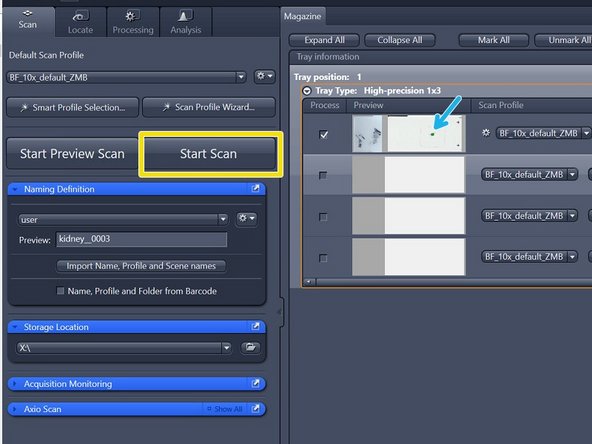
Press "Start Scan"
-
Visualize the resulting image by double-clicking on the slide's preview image after the scan process has been completed
-
Check "Auto" above the histogram to optimize the visualization of the image
-
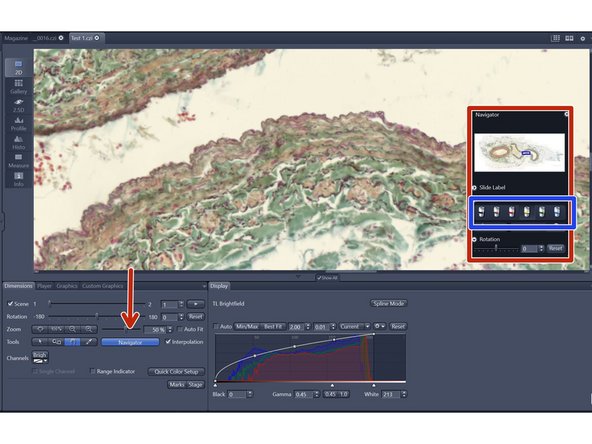
Investigate your image
-
For easier navigation the "Navigator" can be activated
-
Select the imaging lens to visualize the data with an appropriate zoom factor
-
Navigation is also possible with the computer mouse: zoom in / out with the mouse wheel and left click on the image and drag it to move around
-
-
-
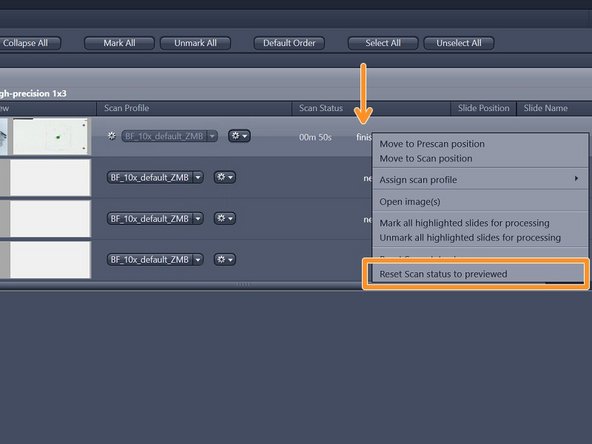
If you are not satisfied with the resulting image, right-click into the scan status "finished"and select "Reset Scan Status to previewed"
-
Go again to "Open advanced wizard" and adjust the parameters
-
Make sure that when you save the same profile twice, you name it different names, otherwise the software has bugs that corrupt the overwritten scan profiles
-
-
-
Select the slides to be scanned. To select all slides click on "Mark All"
-
Select your saved profile in the "Default Scan Profiles" list under "User Documents". The profile will automatically be assigned to all slides that have the "Scan Status" new
-
Click on "Start Preview Scan"
-
After all previews have been captured select "Open tissue detection wizard" and edit the selected ROIs if necessary
-
Press "Next slide" to move from slide to slide
-
Press "Finish" when you are done with the last slide
-
Initiate the scanning of all slides by pressing "Start Scan"
-
-
-
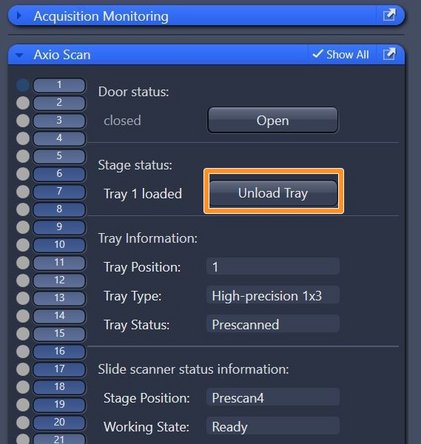
Make sure that all trays are unloaded and take out your slides
-
Close the software
-
After the software has been closed, you have to initiate the transfer of your data following this guide
-
If no other user booked the system after you for that day, switch off the whole system according to the "Shut down" guide . Otherwise, just log-off
-
To visualize the resulting datasets without prior file conversion to .tif, , the software Zen blue, the open source tool QuPath or Imaris can be used. This software tools are available on the ZMB virtual machines
-
To export Zeiss AxioScan .czi files to .tif we recommend to use ZEN blue. See corresponding "Export .czi files to .tif " guide
-
Cancel: I did not complete this guide.
One other person completed this guide.